- Application
- Stone Matrix Asphalt Explained
Stone Matrix Asphalt Explained
At Antrocel, we are your gateway to unparalleled sustainability in the realm of Stone Matrix Asphalt (SMA). As a trusted cellulose manufacturer and supplier, we are rewriting the rules of asphalt road technology by seamlessly integrating cellulose fibers into SMA asphalt. Your journey is defined by making it simply possible, pushing the boundaries of what's possible in asphalt road.

SMA Asphalt best for roads with heavy loads
What is Stone Matrix Asphalt?
Stone Matrix Asphalt, also known as asphalt stone mastic is a type of asphalt blend comprising a carefully balanced mix of coarse aggregates, filler, and binder. It usually includes a stabilizing asphalt additive, commonly known as a drainage inhibitor that prevents the binder from separating from the aggregate. This results in a resilient and durable pavement surface.
The content of SMA Asphalt:
- Coarse Aggregate Skeleton
- Matrix SMA, comprising the binder, filler, fine aggregate, and stabilizing asphalt additive
- Voids present within the SMA asphalt mix.
Imagine a solid stone-on-stone framework that doesn’t just add stability but also amps up mixture strength. Plus, there’s a hardy mortar binder in the mix, working hand in hand with stabilizing agents like cellulose fibers and asphalt modifiers to ensure high durability.
Brief history of Stone Matrix Asphalt
SMA asphalt originated in Germany during the mid-1960s and demonstrated remarkable efficiency in enduring wear and standing up to the challenges posed by studded tires. Due to its exceptional performance, it was officially standardized on a national level in 1984. Subsequently, SMA asphalt gained widespread adoption across Europe and globally.
Application Types:
Stone Matrix Asphalt is suitable for a wide range of applications, including:
- Enhanced Durability The incorporation of cellulose fibers into SMA asphalt significantly improves the overall durability of the asphalt road, extending the pavement's lifespan and reducing maintenance costs.
- Rut Resistance: SMA asphalt's unique composition provides exceptional resistance against rutting, ensuring a smooth and stable road surface even under high traffic volumes.
- Improved Skid Resistance: Cellulose fibers enhance pavement's texture, contributing to better skid resistance and improved safety for drivers.
- Reduced Cracking The presence of cellulose fibers minimizes the occurrence of cracks, reducing the risk of water infiltration and subsequent damage caused by freeze-thaw cycles.
- Environmentally Friendly: Cellulose fibers used in SMA asphalt are derived from sustainable and renewable sources, making it a sustainable choice for road mastic construction.
- Cost-Effective: The enhanced durability and reduced maintenance requirements of mastic asphalt results in long-term cost savings for road authorities and project developers.
- Efficient Maintenance Pace: Thanks to SMA asphalt thin-layer construction, the ease of planning and replacement is a distinct advantage. This translates to minimal traffic disruption during maintenance efforts.
- Good Noise Reduction properties.
Stone Matrix Asphalt Challenges:
- Not Suitable for All Applications: While SMA asphalt excels in high-traffic areas and heavy-load conditions it may not be the best choice for low-traffic roads or locations with unique requirements, where other types of asphalt mixes may be more cost-effective.
- Higher Initial Cost: Compared to conventional asphalt mixes, asphalt mastic can be more expensive to produce and install due to the additional cost of incorporating cellulose fibers and the specialized mix design.
- Complex SMA Mix Design: SMA asphalt requires a precise and complex mix design to achieve its desired performance characteristics. This may pose challenges for some contractors and asphalt producers who are less experienced in working with stone matrix asphalt.
- Cellulose fibers used in SMA asphalt must meet specific requirements and quality standards. As a specialized additive, the availability of high-quality cellulose fibers can be limited, particularly in some regions.
- Fat spot risks in SMA Asphalt Design: It's important to address the potential risk of various types of fat spots emerging on the surface, which can arise due to discrepancies or inconsistencies during the phases of asphalt mastic design, production, or construction.
Working on a certain Asphalt Mix?
Get answers in 1 day
- List Item #1
- List Item #2
- List Item #3
All Products
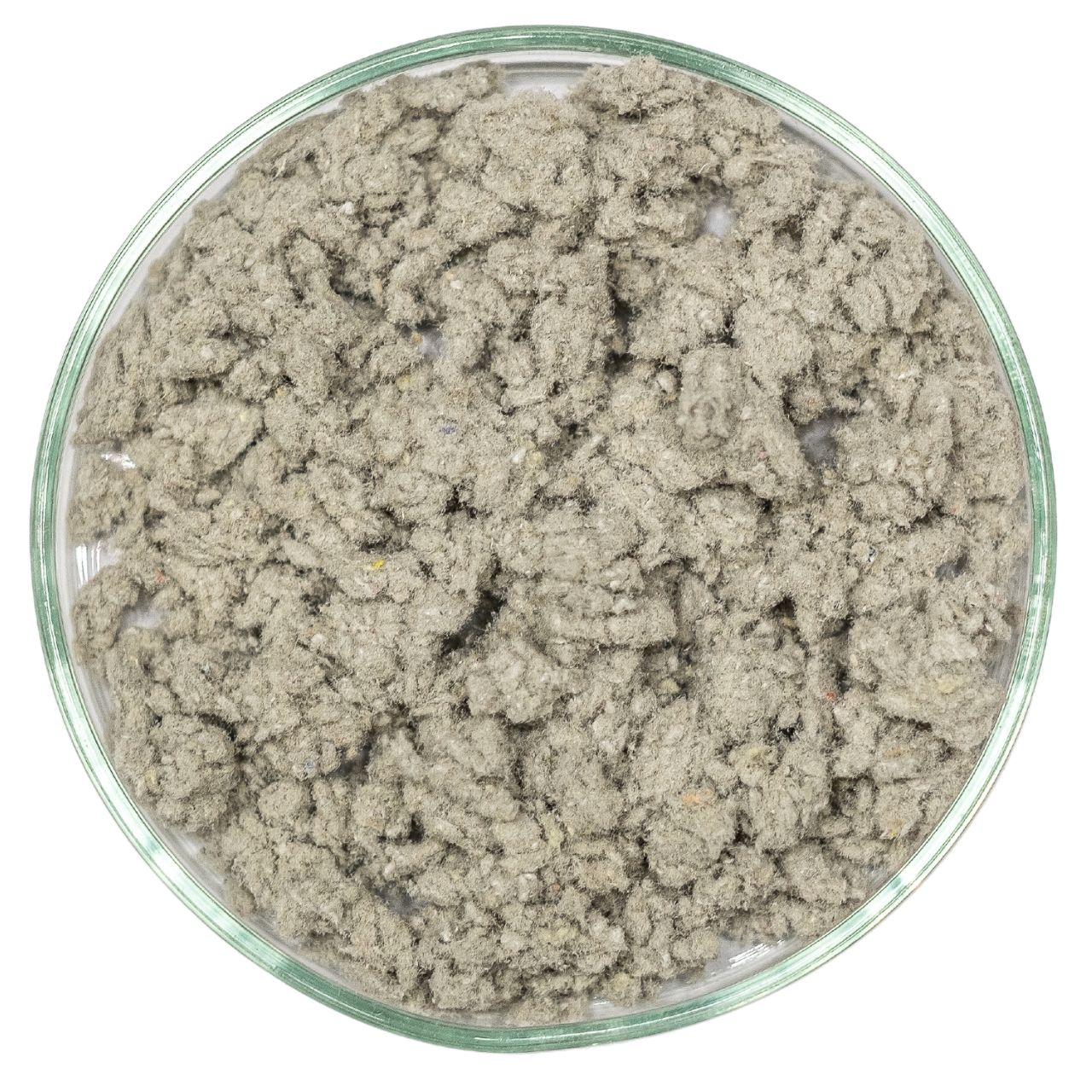

Antrocel-P
Cellulose Fiber for SMA Asphalt Mixtures
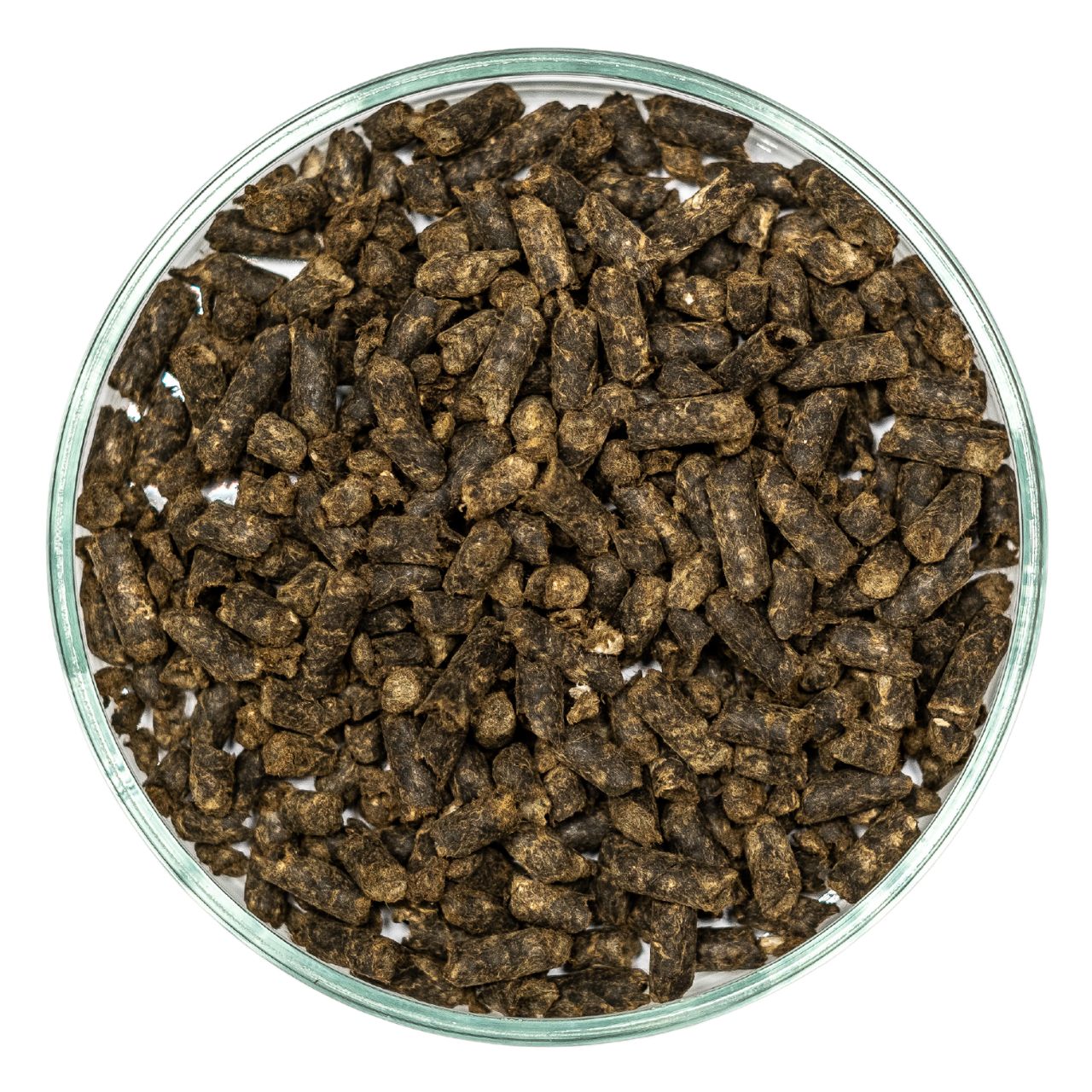

Antrocel-G
Cellulose Fiber Pellets for SMA Asphalt Mixtures
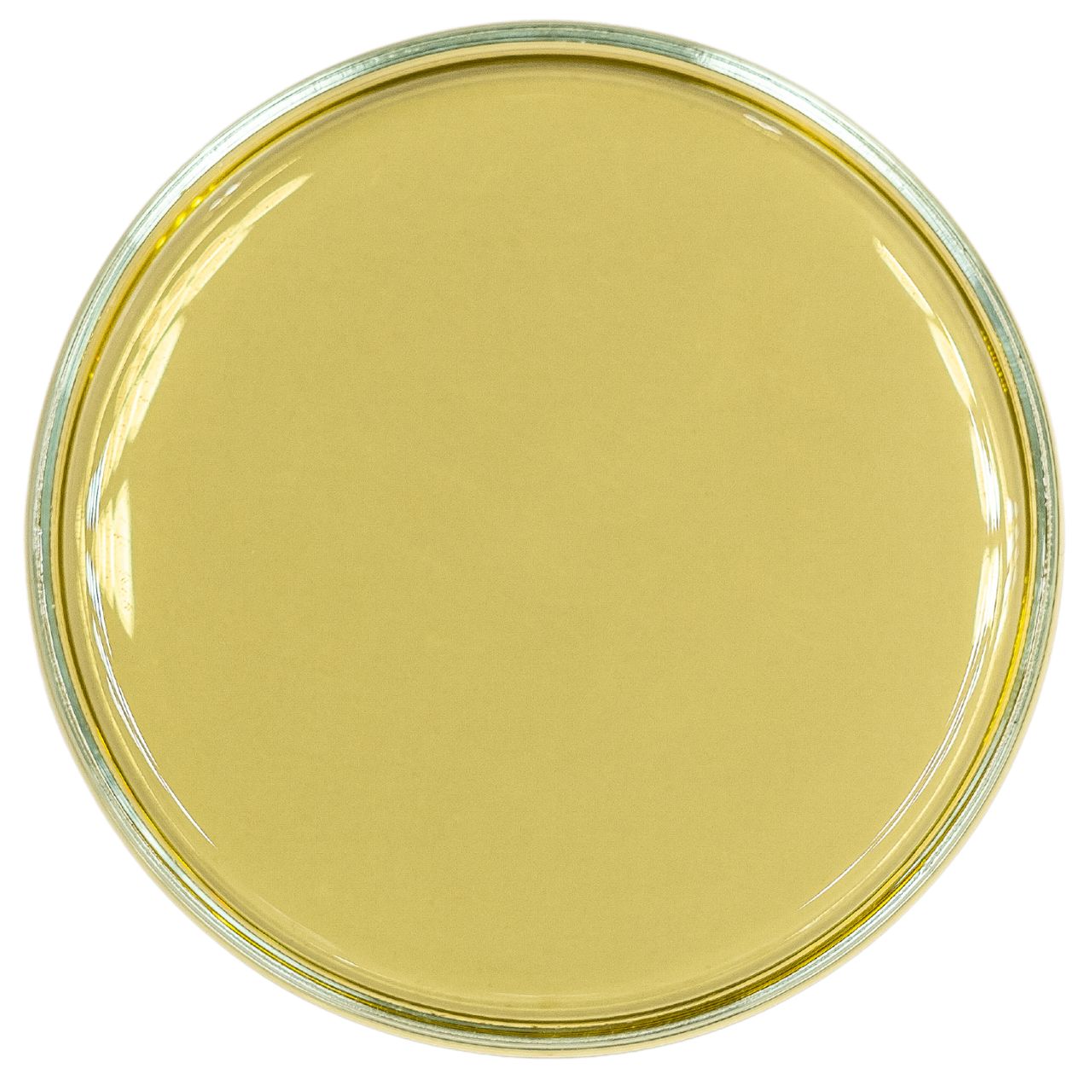

Antrocel-AAK
Anti-adhesive detergent
AntrocelBond
Anti-Stripping Agent for Asphalt Bitumen
